Super gonorrhea is a highly antibiotic-resistant strain of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) gonorrhea that has been spreading rapidly in Nairobi and other parts of Kenya. This strain is particularly concerning because it is resistant to all currently available antibiotics, making it difficult to treat and potentially leading to severe health complications.
The spread of super gonorrhea in Nairobi is thought to be driven by a number of factors, including increased sexual activity, lack of education about safe sex practices, and limited access to healthcare and STI testing. In addition, the high poverty rate in many parts of the city makes it difficult for many individuals to afford the cost of treatment and testing.
The Kenyan government and health organizations have been working to address the spread of super gonorrhea in Nairobi by increasing awareness about the risks of the infection and the importance of safe sex practices. They have also been working to improve access to healthcare and STI testing in the city.
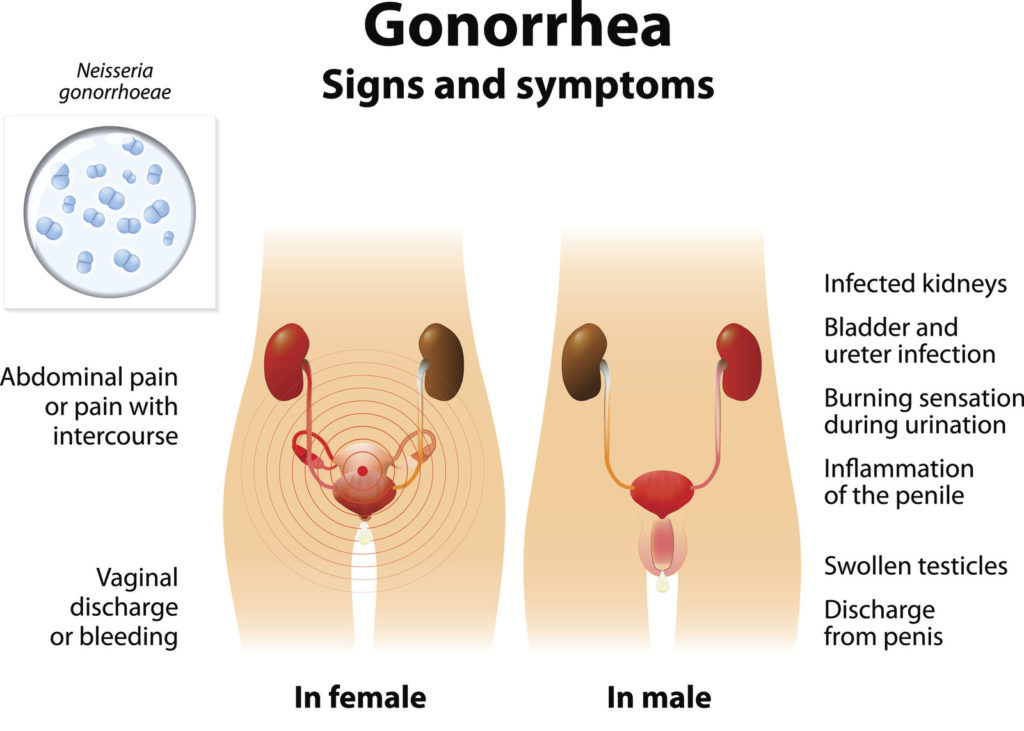
However, due to the highly resistant nature of super gonorrhea, treating and controlling the spread of the infection is a difficult task. In addition, it is also important to address the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to the spread of the infection. This can be done by providing education, improving access to healthcare and testing, and working to reduce poverty.
In conclusion, super gonorrhea is a serious public health concern that is spreading rapidly in Nairobi and other parts of Kenya. It is important for the government and health organizations to continue working to address the spread of the infection and to address the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to its spread. With the right efforts, it is possible to control the spread of super gonorrhea and protect the health of individuals in Nairobi and beyond.



